The best calcium-rich foods to include in your diet
By Louise Belle BHSc (Nut Med)
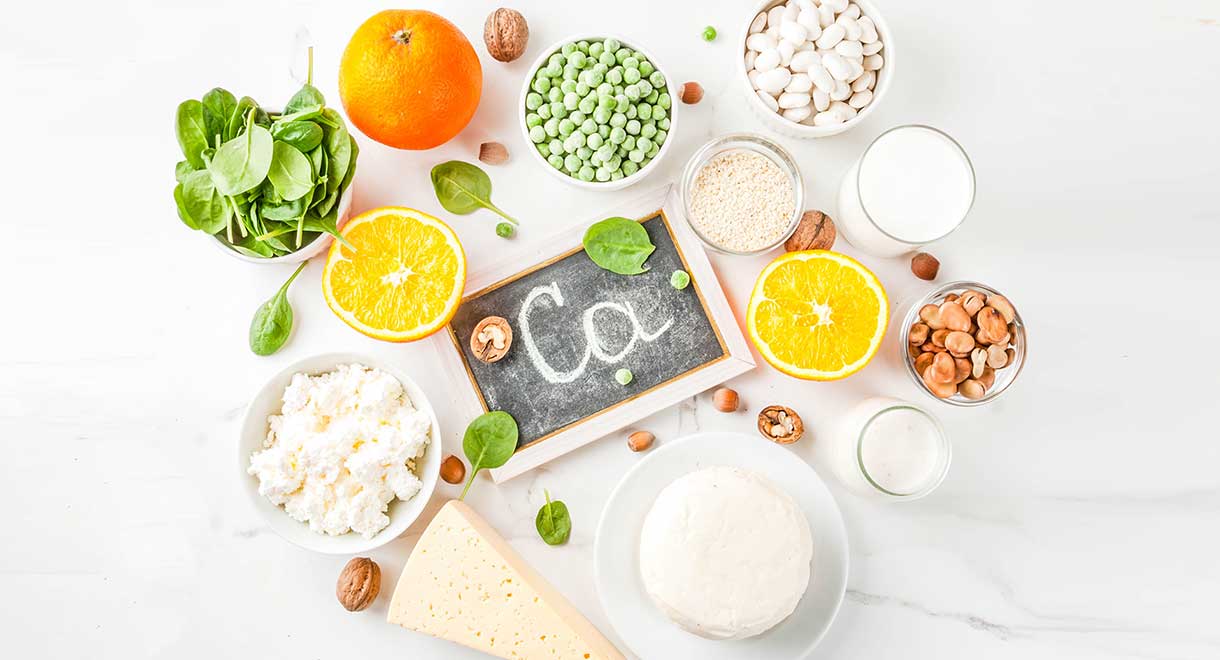
Calcium is the main mineral needed for maintaining and supporting bone strength. Roughly 99% of calcium in the body is stored in bones and teeth. As we age, the risk of osteoporosis (low bone density) increases, but this can also occur in young people. Having low bone density increases the risk of fractures and not consuming enough calcium can slow bone healing. The RDI for calcium is 1100mg daily.






| FOOD | AMOUNT OF CALCIUM |
|---|---|
| Cow’s milk | 1 cup = 300 mg |
| Yoghurt | 200 g tub = 300 mg |
| Bone broth | 1 cup = 300 mg |
| Dried figs | 5 figs = 200 mg |
| Oats | 1/2 cup = 100 mg |
| Leafy greens | 1 cup (cooked) = 180 mg |
| Ricotta cheese | 1/4 cup = 150 mg |
| Sardines | 100 g tin with bones = 300 mg |
| Feta cheese | 40 g = 150 mg |
| Prawns | 100 g = 130 mg |
| Amaranth | 1/2 cup (uncooked) = 150 mg |
| Chia seeds | 1 tbsp = 120 mg |
| Firm tofu | 60 g = 100 mg |
| Tahini | 1 tbsp = 80 mg |
| Calcium Complete tablets | 1 tablet = 282 mg |
Factors reducing calcium absorption
- Tannins in tea and coffee reduce the absorption of calcium when consumed close to a meal. It’s best to leave a gap of 1-2 hours between tea or coffee and your meals/calcium supplement.
- A compound called oxalates in leafy greens can bind to calcium and reduce its absorption. Steaming greens reduces the oxalate content.
- Phytic acid in nuts, needs and grains can reduce calcium absorption. Soaking them overnight can help to deactivate the phytic acid.
- When iron is consumed at the same time as calcium, they can compete for absorption, resulting in less calcium being absorbed. Try having calcium-rich foods (or supplements) away from iron-rich foods (such as red meat) when possible.
- Damage or inflammation in the intestinal lining can reduce our ability to absorb calcium. Gut Health is fantastic at soothing and healing the gut lining.
- Certain medications such as diuretics, antacids and aspirin may reduce levels of calcium in the body.
- Adequate vitamin D levels are needed to transport calcium to the bones. If vitamin D levels are low, calcium cannot be transported.
Factors affecting bone density
Apart from ageing, disease/illness, low oestrogen levels (post-menopause) and the factors mentioned above, eating an acidic diet can have a negative impact on bone health. When you consume too many foods that are acidic to the body (such as soft drink, bread, fried foods) and not enough alkaline foods (such as fruit and vegetables), the body compensates by leeching minerals from the bones to balance pH. The Dr Cabot Cleanse contains an alkaline diet to reduce acidity in the body. Lack of exercise is another cause of low bone density. Weight bearing exercise like running, skipping and weight lifting are the best for building bone density.

Cofactors needed for strong, healthy bones
- Vitamin D3
- Magnesium
- Vitamin K2
- Boron
- Zinc
- Manganese
- Copper
All these ingredients are included in our Calcium Complete tablets.









Leave A Comment