The best and worst foods for inflammation
By Nutrition Consultant Jessica Robinson
Simply put, inflammation refers to your body’s physiological response from the immune system to facilitate healing of an injury or any sort of attack upon your tissues. Physically, inflammation is felt as swelling, redness, heat and pain. Inflammation can be caused by an excess amount of free radicals or oxidation in our cells, and becomes more common as we get older and our immune system becomes more susceptible to inflammation. Chronic inflammation or unresolved inflammation is the real concern that can cause tissue destruction, leading to degenerative diseases, scar tissue and premature ageing.
There are many possible causes of excessive inflammation such as autoimmune genes, a poor diet, leaky gut, fatty liver, mechanical trauma, wear and tear on the joints, adrenal insufficiency, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, certain viruses, chronic infections and inflammatory hormones.
The mineral selenium has anti-inflammatory properties and helps to relieve inflammation.
Here are some foods to steer clear of if you want to avoid inflammation:


Sugar
Is found in foods such as white rice, white bread, white flour, noodles, cereals, baked goods, pasta and biscuits. These are refined grains which are sources of empty calories, this means that they are high in calories but are devoid of nutritional value. Excess sugar can cause elevated insulin levels that results in our blood sugar levels to plummet which ultimately causes inflammation.


Dairy
The thing is, humans don’t need milk and the majority of the population lack the necessary enzymes to properly digest milk. If you eat dairy and suffer from symptoms such as bloating, gas, diarrhoea, constipation, intestinal distress, or any other negative side effects, this may indicate that you are sensitive to lactose. If this is the case, we recommend you eliminate dairy from your diet altogether. For many people, milk is an allergen which can trigger inflammatory responses, so be sure to monitor your tolerance.


Trans fats
Are found in deep fried foods, baked goods, processed foods and foods prepared with margarine and/or hydrogenated oil. Trans fats should definitely be avoided as not only do they increase ‘bad’ cholesterol and lower ‘good’ cholesterol, but they also cause inflammation, insulin resistance, obesity and their consumption can lead to degenerative illnesses. If you want to promote good health, it is best to steer clear of these bad boys.


Artificial food additives
Ingredients such as aspartame and monosodium glutamate (MSG) can trigger inflammatory responses and contain chemicals that are potentially toxic to the nervous system. Reports have proven that these chemicals can increase inflammation and flare-ups in people with conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.


Processed/Commercially produced meat
Commercial animals are often grain-fed with diets that are high in omega-6 fatty acids and low in omega-3 fatty acids. They gain fat as they are kept in enclosed conditions and this results in products that are lower quality, have less nutritional value and have inflammatory effects on our bodies. Many animals are also injected with hormones and antibiotics which contributes to inflammation in the animal that can later affect the consumer.
Here are some foods that fight inflammation:
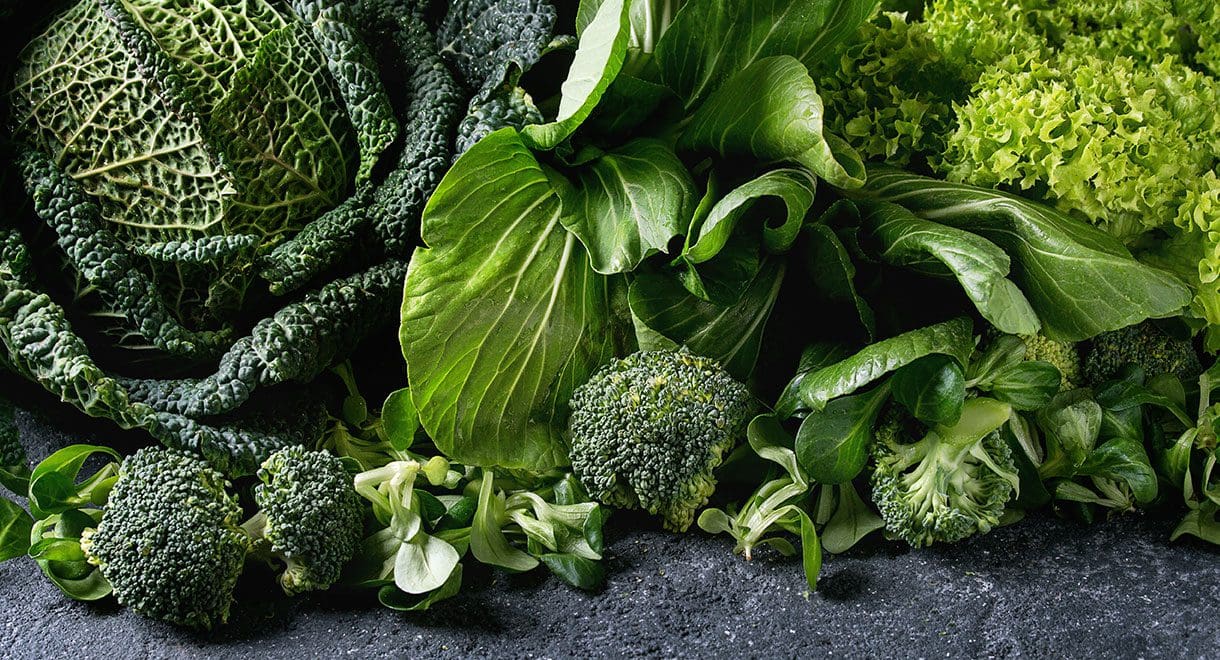


Dark leafy greens
Vegetables such as kale, cabbage, spinach, broccoli and Bok choy are nutritional powerhouses that are loaded with antioxidants as well as rich sources of vitamin A, E, K and C. Regularly consuming these foods is a sure way to combat inflammation, restore cellular health and promote overall wellness.
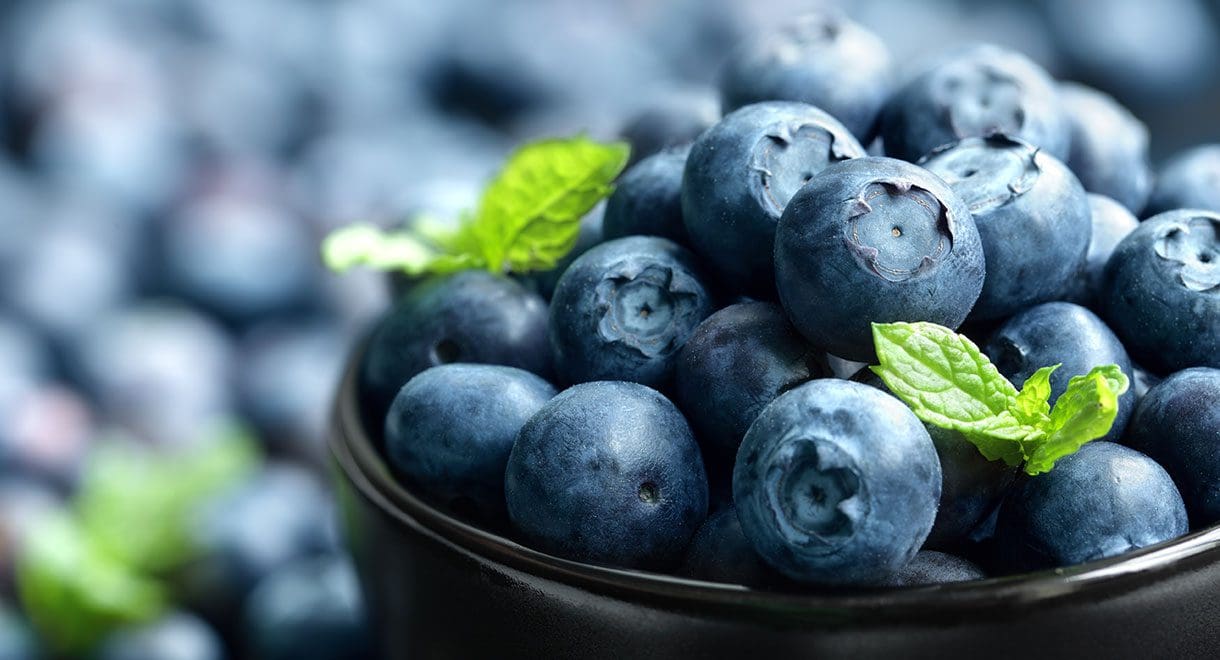


Blueberries
These small blue fruits are bursting with antioxidants that protect the body from oxidative stress and reduce inflammation. Studies have also proven that consuming more blueberries slows cognitive decline and boosts brain and mental health. Aim to have ½ a cup a day to reap the benefits.
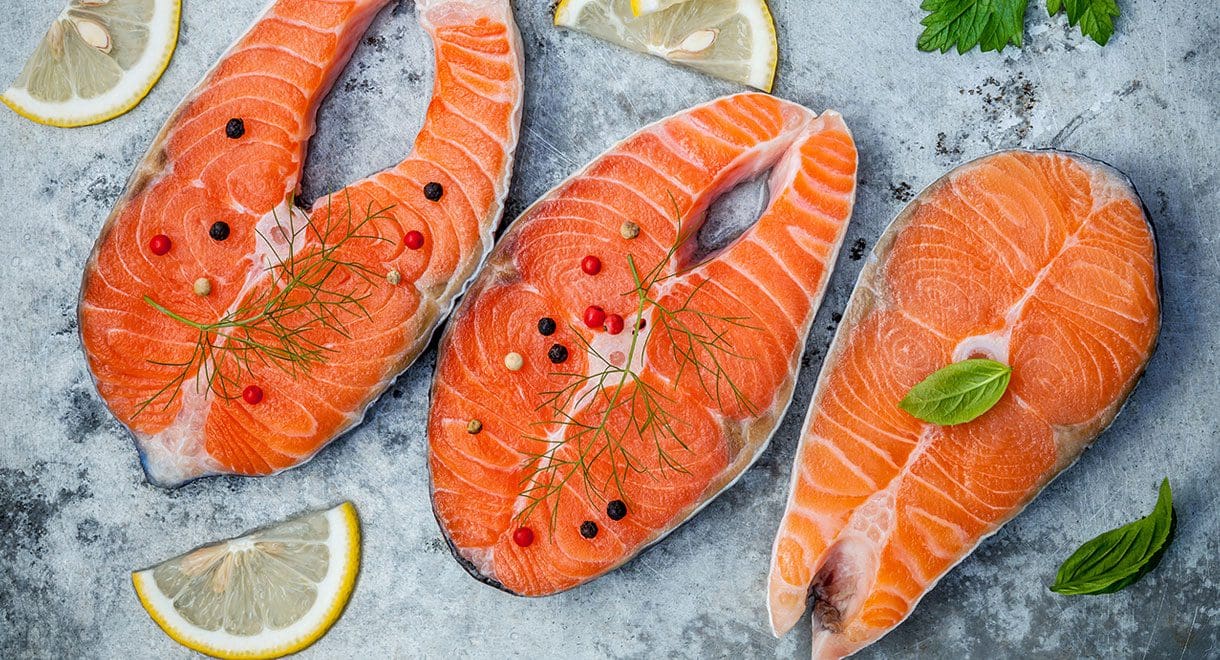


Fatty fish
Oily fish such as mackerel, salmon, sardines and tuna boost omega-3 fatty acids which reduce inflammation and may even lower your chances of chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer and arthritis. Omega-3s are some of the most powerful anti-inflammatory substances and as they are highly concentrated in the brain, it is essential to get adequate amounts to support healthy cognitive and behavioural function.


Coconut Oil
This product has got to be one of the most versatile, and has many benefits for your skin, hair and internal system. The fats in coconut oil are loaded with anti-inflammatory properties and according to a study in India, the antioxidants in coconut oil were more effective at healing arthritis and other inflammatory problems than leading medicines. Although coconut oil is extremely healthy, it is also pure fat so you should consume no more than a teaspoon a day.
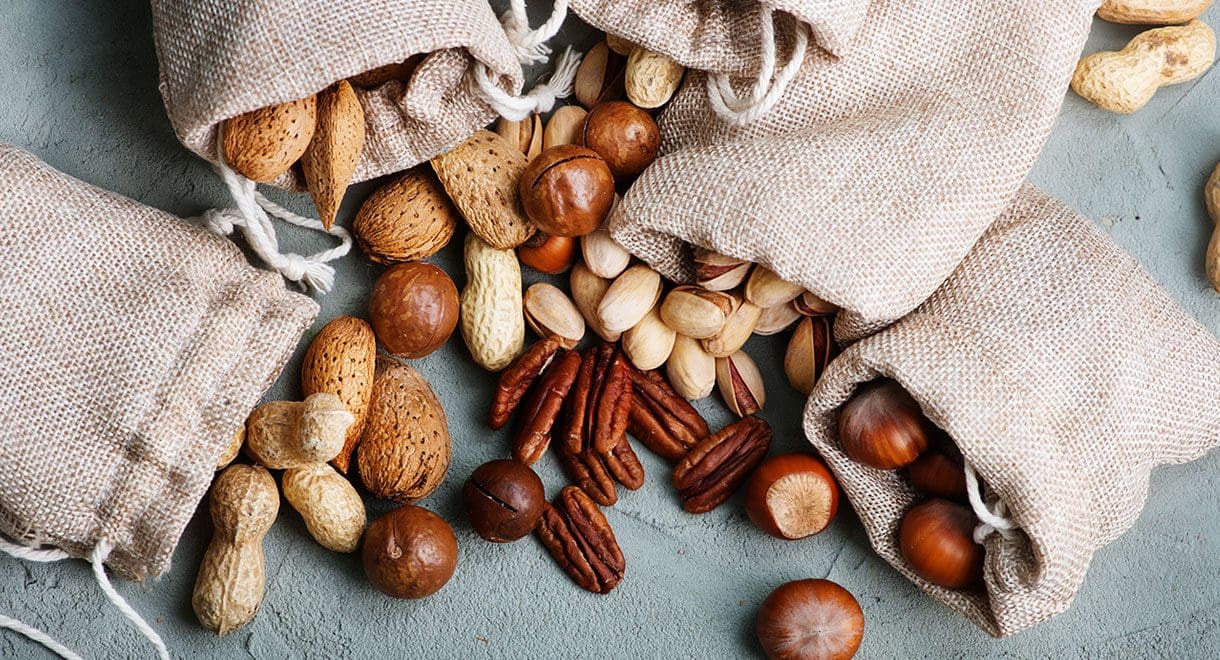


Raw nuts and seeds
Nuts must be fresh and good choices include almonds, macadamia, pine nuts, hazelnuts, pistachio, cashews, walnuts and Brazil nuts. Good seeds to add to your diet include flaxseeds (linseeds), sunflower, sesame, chia, hemp seeds and pumpkin seeds. Nuts and seeds are great sources of protein and healthy fats and are filled with antioxidants to reduce inflammation throughout the body.
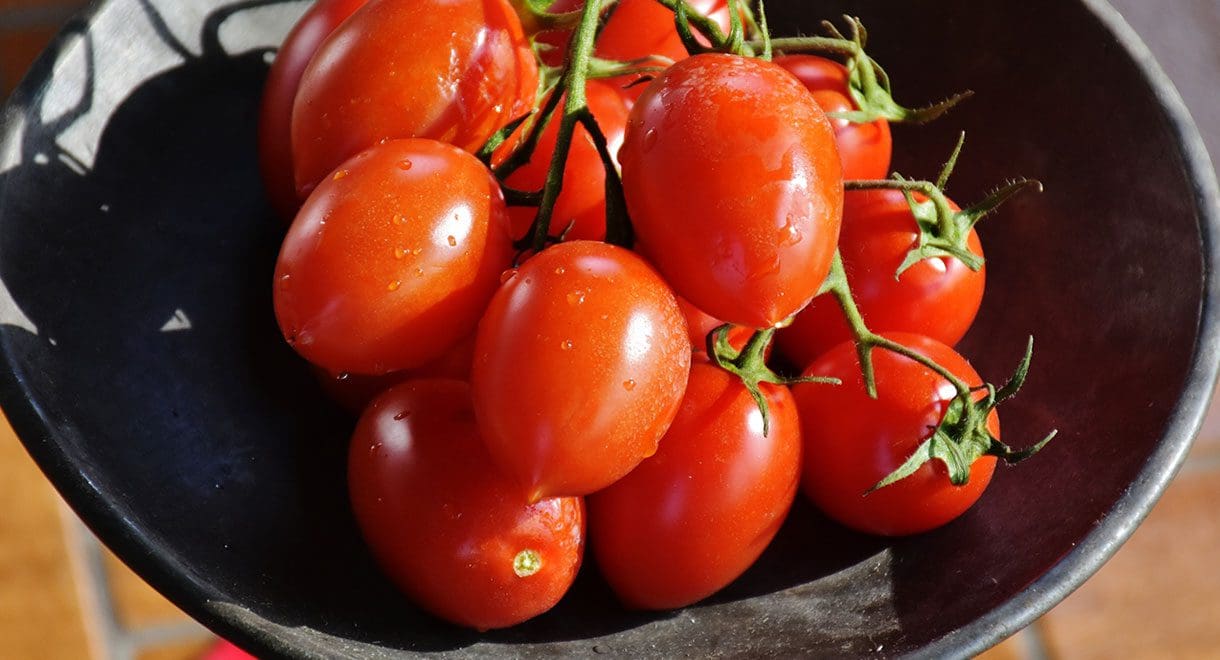


Tomatoes
Tomatoes are a rich source of lycopene which is known to reduce inflammation in the body and lungs. Cooked tomatoes contain more lycopene than raw tomatoes. A 2013 study discovered that tomato juice was beneficial for reducing systemic inflammation.
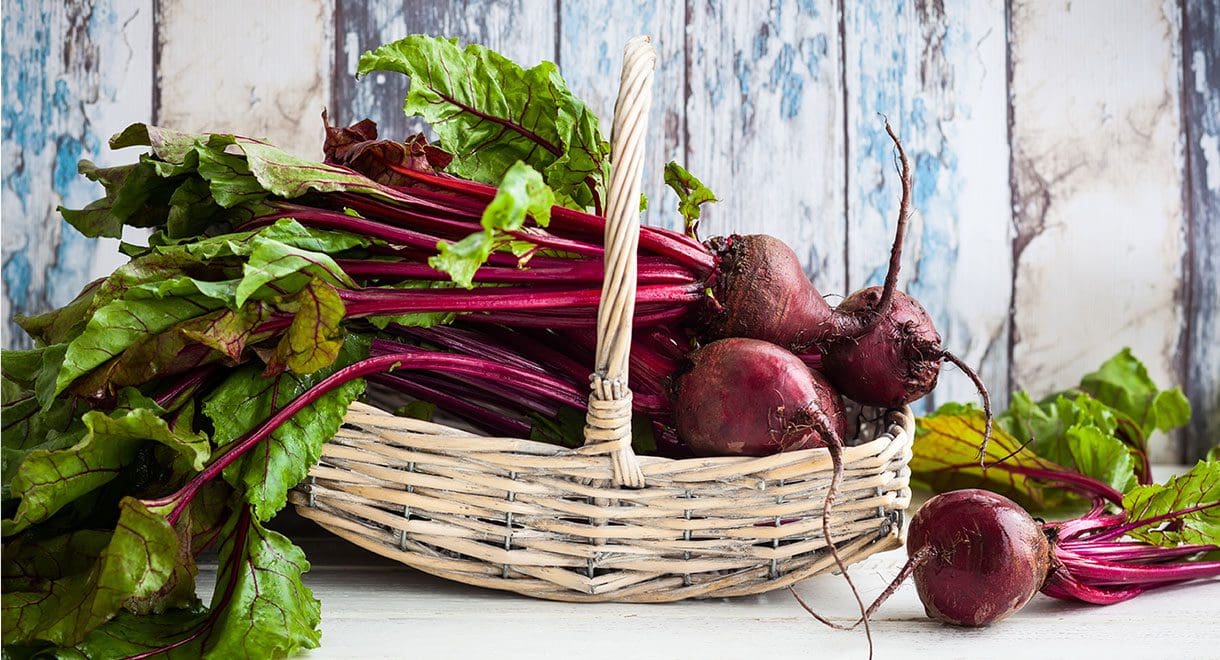


Beets
Their deep purple colour is caused by the antioxidant betalain, which is known to be an amazing anti-inflammatory. Dietary benefits include repairing cell damage and providing high levels of inflammation-fighting potassium and magnesium. Due to its high amount of fibre and folate it also protects against heart disease and cancer.
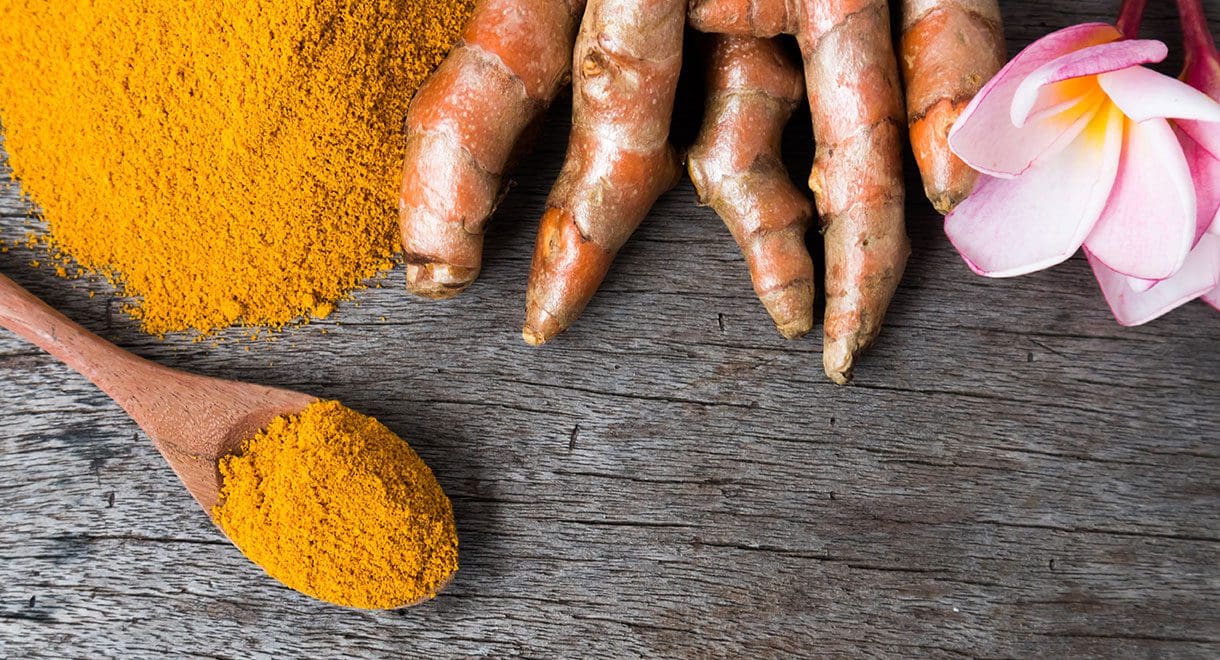


Ginger and turmeric
Many studies have proven that these spices contain anti-inflammatory properties. Curcumin is the compound found in turmeric that is its active anti-inflammatory component. A study discovered that curcumin is a lot more powerful than aspirin and ibuprofen as an anti-inflammatory. Used fresh, dried or in supplement form, ginger helps to reduce inflammation and is especially beneficial for arthritic pain, muscle pain and improving movement agility.
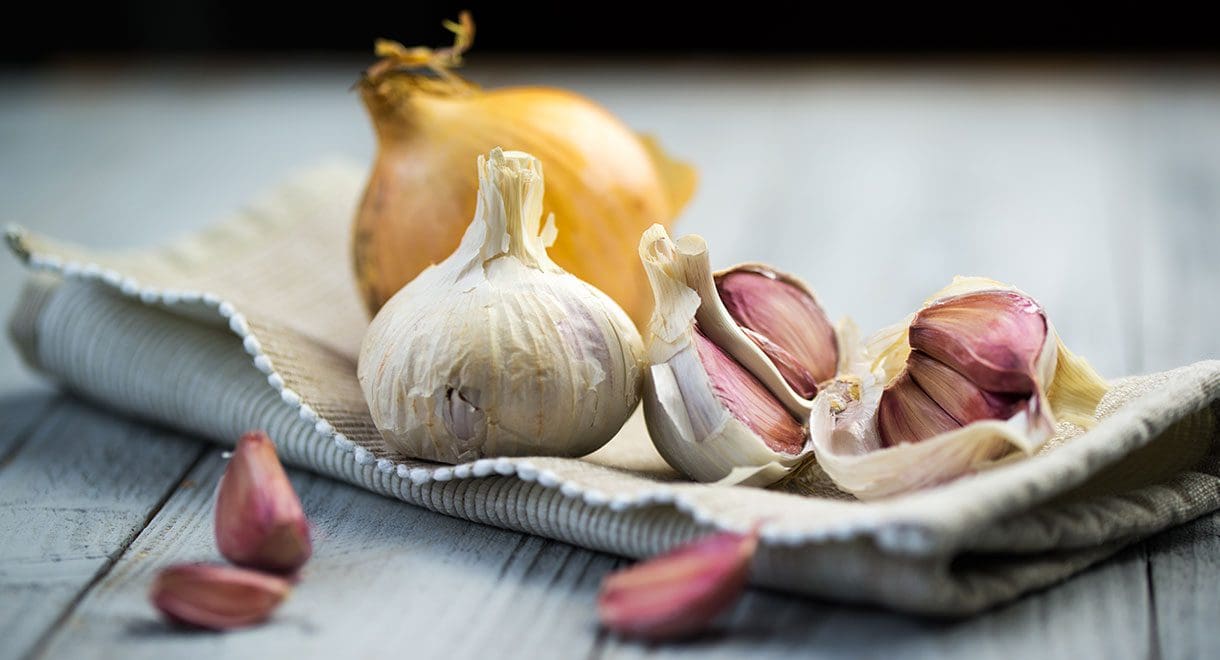


Garlic and onions
These pungent vegetables also happen to be prebiotics which means they feed good bacteria in the gut and are also highly anti-inflammatory. The compounds in garlic reduce substances that cause inflammation, and onions obstruct the agents that promote inflammation in arthritis. It is most beneficial to consume garlic raw.
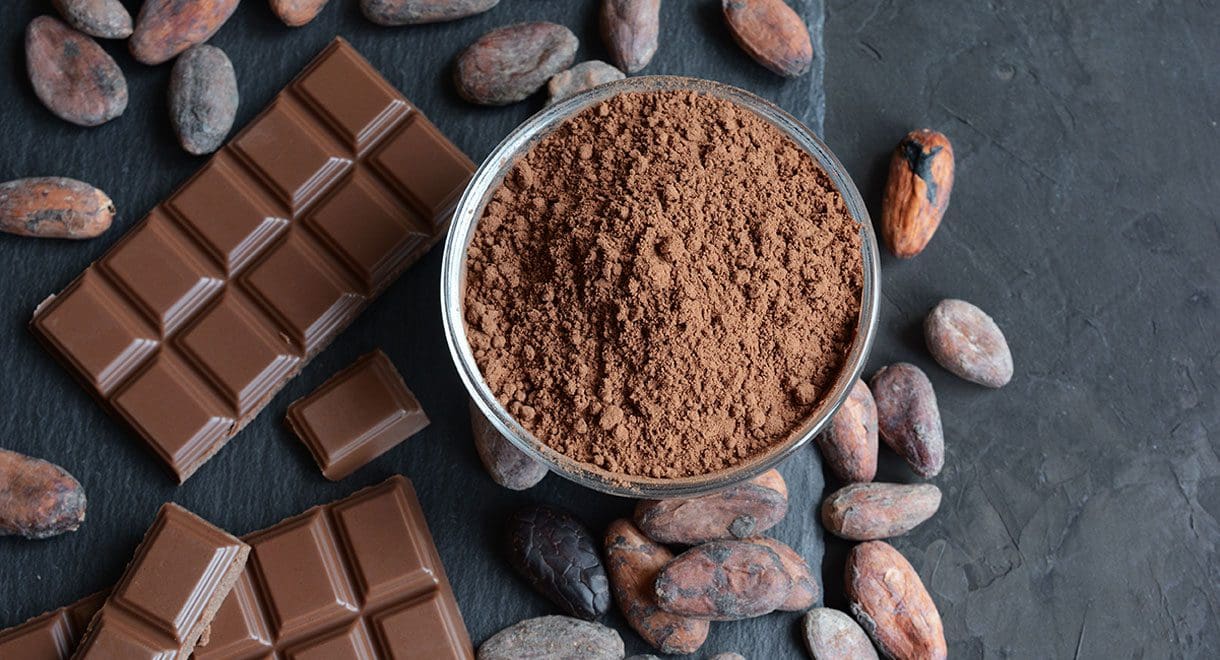


Dark chocolate
Not only is dark chocolate delicious and satisfying, it is also loaded with antioxidants to reduce inflammation and provide a guilt-free treat. Recent research has revealed that gut bacteria ferments and breaks down the components in dark chocolate which allows their anti-inflammatory properties to take effect. To obtain these benefits, you must choose a dark chocolate that contains at least 70% cacao.
For more information and tips on reducing information, check out Dr Cabot’s book ‘Healing Autoimmune Disease’.





please write an article on salicylate intolerance. all these foods are high in salicylates – so what we sufferers eat?
Hi Annie,
Thank you for your article suggestion, we will keep it in mind.
There are many food lists available online in the meantime.
Kind regards,
Louise
Hi Louise,
I hope you Dr Sandra and all the Team are all well and I want to wish you all a great time at Christmas. I will be going to the Farm.
I have just become a great Nanna , Harry is very cute, 3 weeks premmy and now 7 weeks old..
I am pleased to say I have my sarcoidosis inactive presently, but it left my lungs pretty scarred .and have Sjogren’s syndrome, so now researching what to eat and not to eat to rid this lol!
I read that Selenium is good to keep the inflammation down. I keep of Dairy and gluten.
I still miss you lovely people. hugs to you all. will ring up shortly for more drugs lol!)
love reading you healthy ideas
Albertha X
Hi Albertha,
Glad to hear that everything is going well for you and that you are now a great nanna – how exciting!
That’s fantastic that your sarcoidosis is inactive. The diet in the book Healing Autoimmune Disease will help your Sjogrens, but it sounds like you are already on the right track 🙂
We miss your smiling face around here!
Take care,
Louise