Inflammation may raise your cancer risk
Everyone wants to do what they can to avoid cancer. Did you know that having too much inflammation in your body is a strong risk factor? Inflammation can cause wear and tear to all areas of your body. It can damage the genetic material in your cells and inside your mitochondria. This can interfere with proper cell function, potentially causing cancer.
What is inflammation?
Inflammation is the way our body responds to injury. We can usually tell a part of our body is inflamed when it is red, hot, swollen and we can’t move it properly. Think of a stubbed toe or a sprained ankle. Inflammation is present in all ‘itis’ conditions, such as arthritis, hepatitis, bursitis, and many others. However, inflammation can also occur inside our body in a much more subtle way, where we don’t even know it is happening. Fatigue and pain are classic indicators that there’s too much inflammation in your body.
Type 2 diabetes raises inflammation
Elevated blood sugar, elevated insulin, fatty liver and obesity all contribute to raised inflammation. People with these conditions are at higher risk of cancer, especially breast, kidney, uterine, thyroid, ovarian, gastrointestinal cancers and multiple myeloma. This is because they have chronic low grade inflammation in their body for years.
Researchers recently wanted to test whether the blood markers of inflammation IL-6 (interleukin 6), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) can predict the development of obesity related cancers in patients newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes.
Among 6466 patients, 327 developed obesity related cancers over a median period of 8.8 years. The scientists discovered that each standard deviation increase in IL-6 levels increased the risk for obesity related cancers by 19 percent.
The researchers did not find a strong association between TNF-α or hsCRP and obesity related cancers. Therefore a blood test for interleukin 6 may be a useful test for type 2 diabetics to assess levels of inflammation and cancer risk.
Which conditions raise inflammation?
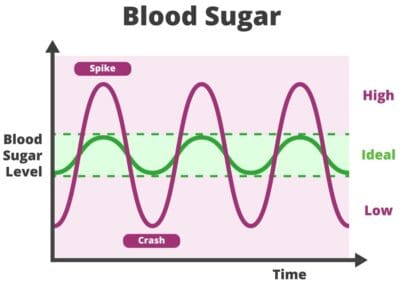
Elevated blood sugar
This can occur in type 1 or type 2 diabetics as well as non diabetics if they eat a lot of carbohydrate and experience a glucose spike. Regularly consuming sugar, grains and high glycemic foods will flood your bloodstream with glucose. Sugar is sticky and it can bind to proteins in your body and damage them.
Infections
Any type of bacterial, viral, fungal or parasitic infection raises inflammation, because your immune cells produce massive quantities of inflammatory chemicals as they try to fight the infection. This is particularly a problem in chronic, long term infections.

Food allergy, intolerance and sensitivity
Whenever you consume a food you are sensitive to, your body behaves as though you swallowed something harmful. As your immune system tries to cope with this scenario, it produces a host of inflammatory chemicals. This can become a significant problem if you unknowingly eat this food(s) every day.

Lack of sleep
Good solid sleep is one of the most powerful anti-inflammatory remedies there is, and it’s free and feels great. Unfortunately most people know this but try as they might, they can’t get good sleep consistently. Insomnia or just poor quality sleep is endemic in modern society.
Injuries
Accidents and surgery are a major physical stress on the body, and these processes all generate a great volume of inflammatory chemicals. These inflammatory chemicals are very useful in acute conditions and are necessary for the recovery process. Unfortunately many patients are left with chronic pain, swelling and immobility because the inflammatory process has continued for too long.







Leave A Comment