Are you tired because of a sluggish liver?
By Dr Sandra Cabot
The liver is the largest internal organ in the human body, and is a central processing factory for everything absorbed from the digestive tract. It receives a double blood supply, with the portal vein bringing nutrient-laden blood directly from the intestines, which makes the liver the major organ of metabolism.
The liver is the gateway to the rest of the body and this allows the liver to regulate the chemical composition of blood before it circulates back to the heart and is then pumped around the whole body. All the biochemical processes are performed by specialized cells in the liver called hepatocytes.
The liver creates energy
The liver manages the body’s energy supply, and the Chinese call the liver The General of the Army of the Body. The liver regulates carbohydrate metabolism and when glucose rises after a meal, the liver converts the excess sugar into a storage form called glycogen. This is critical as it prevents blood sugar levels from going too high after eating. Inbetween meals the liver turns its stored glycogen back into sugar and it is released back into the bloodstream to maintain a steady blood glucose level. This maintains energy and reduces cravings for sugar and stimulants.
The liver can also make its own new glucose ( a process known as gluconeogenesis) from non-carbohydrate sources like lactate, amino acids, and glycerol. This provides a continuous energy supply for the brain if glycogen stores become low. Thus, you do not have to eat regular amounts of carbohydrate to stay energised.
The liver also regulates fat metabolism and fat storage by converting excess carbohydrates and amino acids into fatty acids. These fatty acids are stored as triglycerides in your liver and fatty areas of your body. So its very easy to become overweight by eating excess carbohydrates.
The liver manufactures cholesterol which is critical for healthy cell membranes, and the production of steroid hormones and bile. The liver regulates the cholesterol levels in the blood.
The liver regulates protein metabolism and converts highly toxic ammonia into urea which is excreted by the kidneys. If ammonia levels rise you will have mental fatigue and brain fog.
Manufacture and Secretion of Essential Compounds
The liver acts as a major manufacturing and secretory gland, producing a diverse range of proteins and compounds that are exported throughout the body. It makes bile acids from cholesterol and the bile is secreted into the intestines to enable the absorption of fats and fat-soluble vitamins.
The liver makes clotting factors which prevent you from bleeding to death. The liver contributes to blood pressure regulation through angiotensinogen production.
The liver makes Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1), which stimulates cells throughout the body to grow, proliferate, and build proteins. So, a healthy liver is essential to maintain muscle and bone mass and strength.
The liver regulates the transport of fats in the blood stream and makes lipoproteins such as very-low-density lipoproteins (VLDL) and high-density lipoproteins (HDL). These particles transport triglycerides, cholesterol, and other lipids between different body tissues.
Detoxification and Clearance of Waste
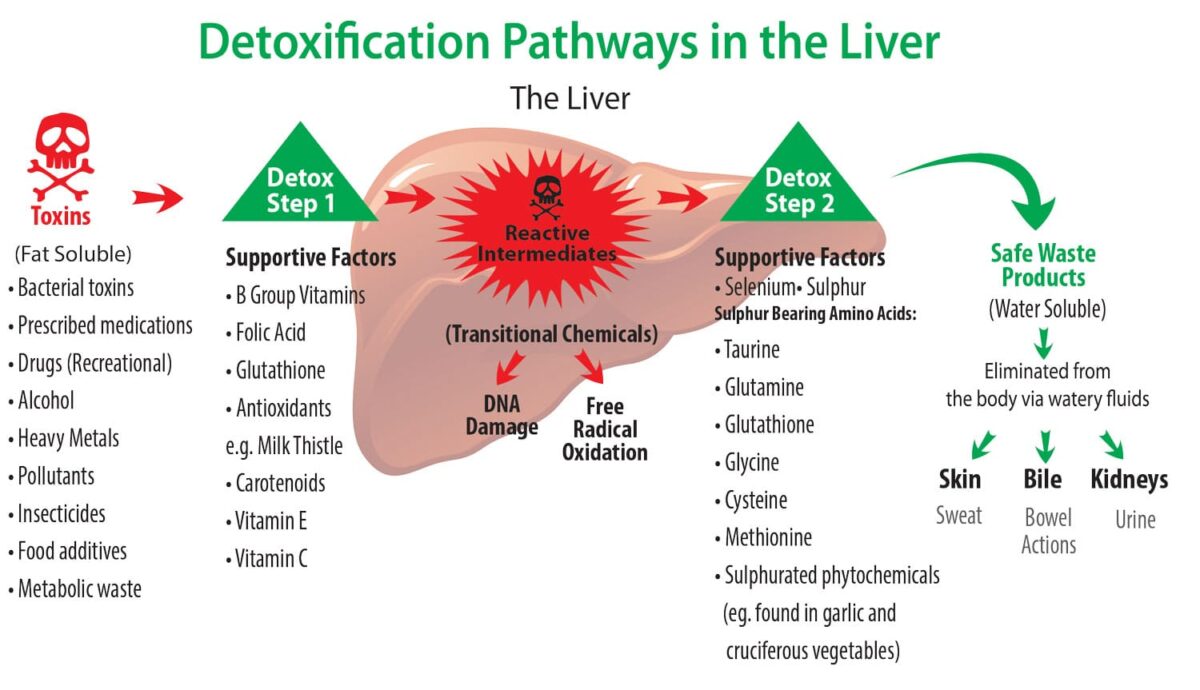
The liver removes and neutralizes substances that are toxic to the body. The liver cells contain a complex system of enzymes, (called cytochrome P450 enzymes) which can inactivate medications and other foreign substances so they can be excreted in urine, bile, sweat and saliva.
The liver processes the waste products from the breakdown of old red blood cells through bilirubin conjugation and excretion. It takes unconjugated bilirubin, a yellowish pigment, and chemically links it to glucuronic acid, making it water-soluble so it can be excreted into the bile and eliminated from the body.
The liver is a great protector
The liver is a physical filter which removes unhealthy cells and debris from the blood stream. The liver contains immune cells (Kupffer cells) which chew up rubbish and fight infection. The liver protects your immune system from overload.
Storage and Hormonal Regulation
The liver is a warehouse for the nutrients vitamins A, D, E, K, B12 and the minerals iron and copper.
The liver helps to balance hormones by breaking down and clearing excess circulating hormones, including sex steroids, insulin, and thyroid hormones.
Because the liver is so busy working 24/7 this metabolic activity generates heat which maintains body temperature at safe levels.
For more information about liver health see our books The Liver Cleansing Diet and Fatty Liver: You Can Reverse It.






Leave A Comment